3.1 Light
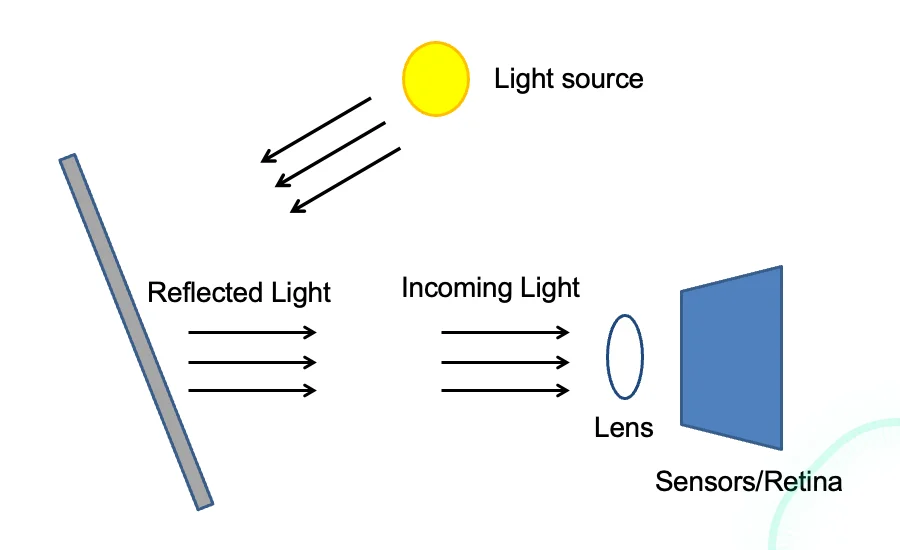
Introduction to Light and Color Perception
- We perceives color from the complex interacction of multiple factors
Factors Determining Perceived Color
- Material properties (albedo / reflectnace)
- Surface Geometry (angles, shadows, highlights)
- Illumination specturm (color temperature of light source)
- Viewing conditions (adaptation state, surrounding colors)
albedo: the proportion of the incident light or radiation that is reflected by a surface, typically that a planet or moon
Mathematical Representation:
where:
- : reflectance (material property)
- : illumination intensity
- : geometric fctors (surface, angles)
The Eye
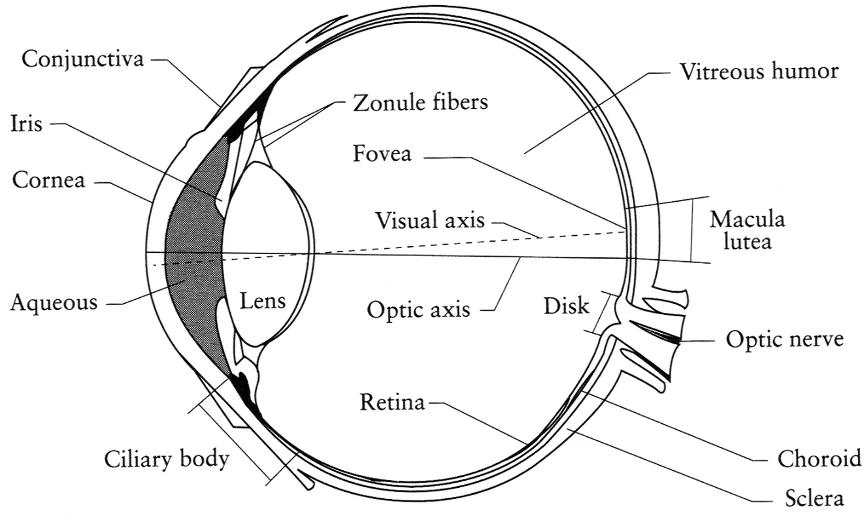
| Eye Component | Camera Equivalent | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Iris | Aperture diaphragm | Spans and contracts pupils to control light amount |
| Pupil | Aperture opening | Light entry point |
| Lens | Camera lens | Focuses light |
| Retina | Image sensor/film | Detects light |
| Optic nerve | Data cable | Transmits signals |
Retinal Structure
- The retina is NOT a simple light-detection surface. Light must pass through multiple layers.
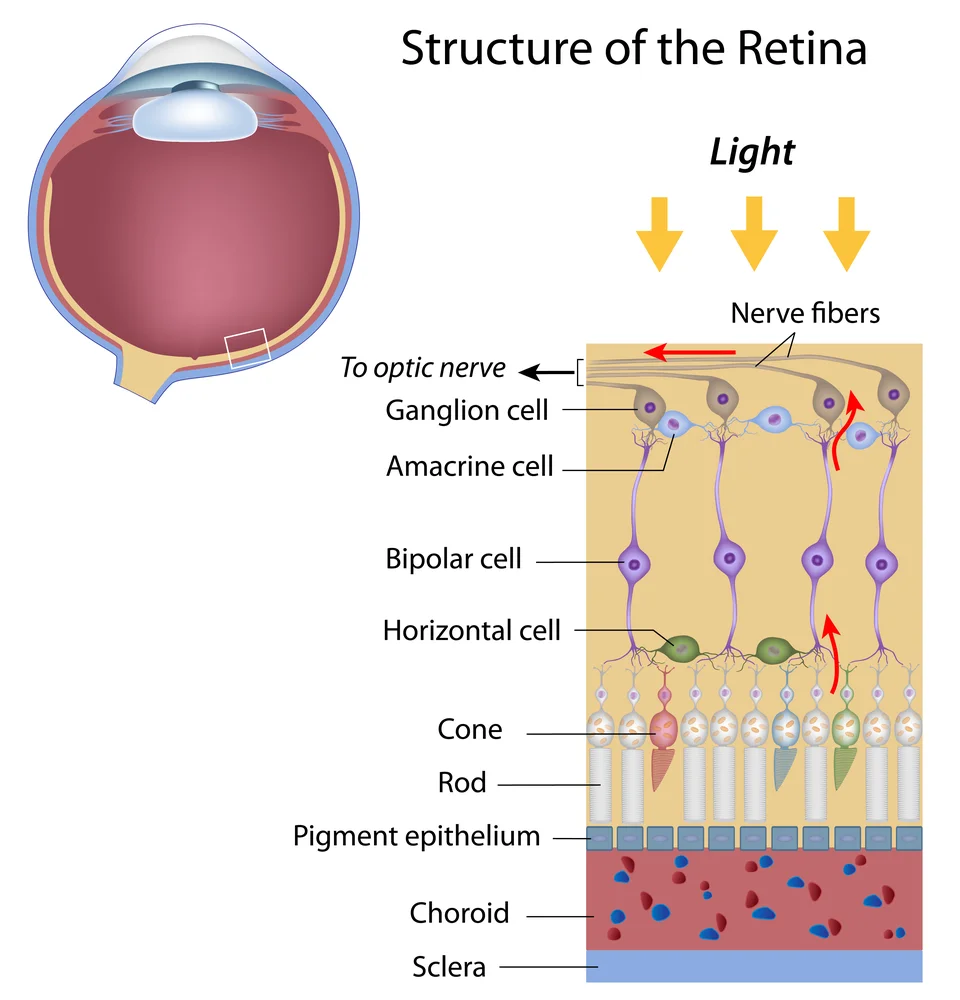
- Ganglion cells
- First layer light encounters
- contrast-sensitive
- control iris response
- process initial visual information
- Bipolar and horizontal cells
- Intermediate processing layers
- handle lateral inhibitation (edge enhancement)
- contribute to automatic responses (blink reflex)
- Photoreceptors
- Rods and cones for actual light detection
- Convert photons to electrical signals
- Foundation of all vision
Important
This backwards arrangement means light is partially filtered and processed before reaching phtoreceptors
Phtoreceptors: Rods and Cones
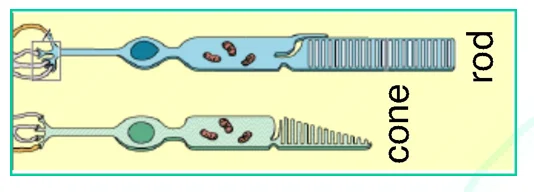
- Humans have two separate visual systems operating simultaneously.
| Feature | Rods | Cones |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Vision in low light, peripheral vision, motion detection | Color vision, central vision, and detail acuity |
| Light Sensitivity | High; active in dim light | Low; active in bright light |
| Color Perception | Responsible gray-scale vision | Responsible color vision |
| Distribution | More numerous and concentrated in the periphery of the retina | Less numerous and concentrated in the center of the retina |
| Detail Acuity | low | high |
LMS cone cells
- OPN1LW
- (long-wavelength, red)
- X chromosome
- OPN1MW
- (medium-wavelength, green)
- X chromosome
- OPN1SW
- (short-wavelength, blue)
- chromosome 7
Surface
Lambertian Surface
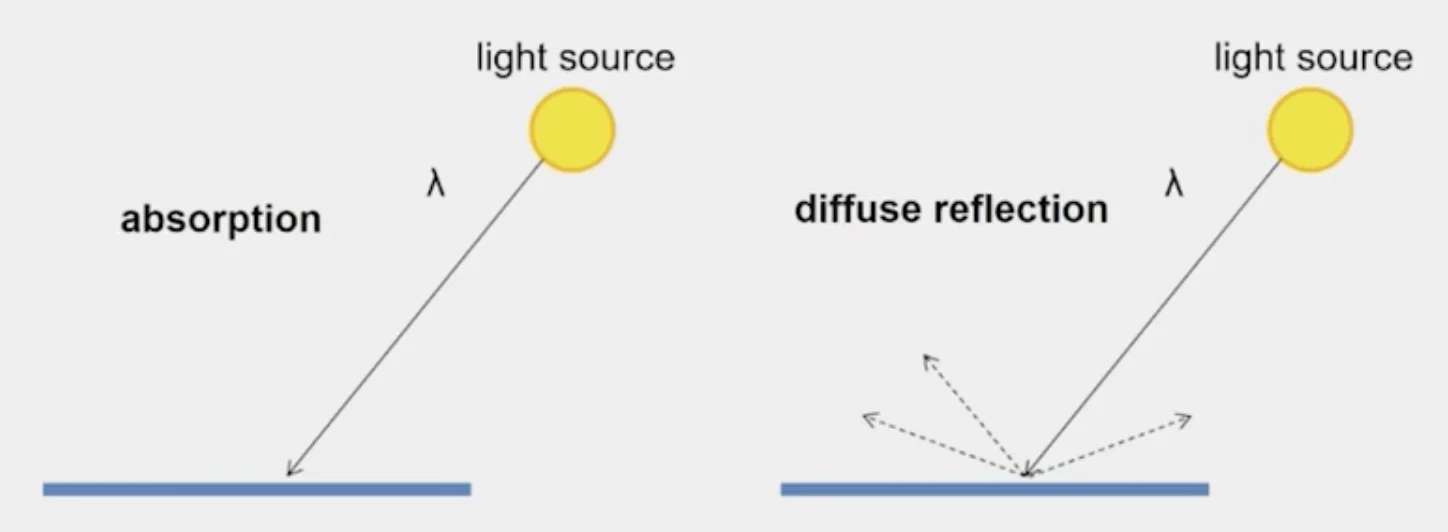
- Some light is absorbed
- albedo
- Remaining light is reflected in all directions
- diffuse reflection
Diffuse reflection
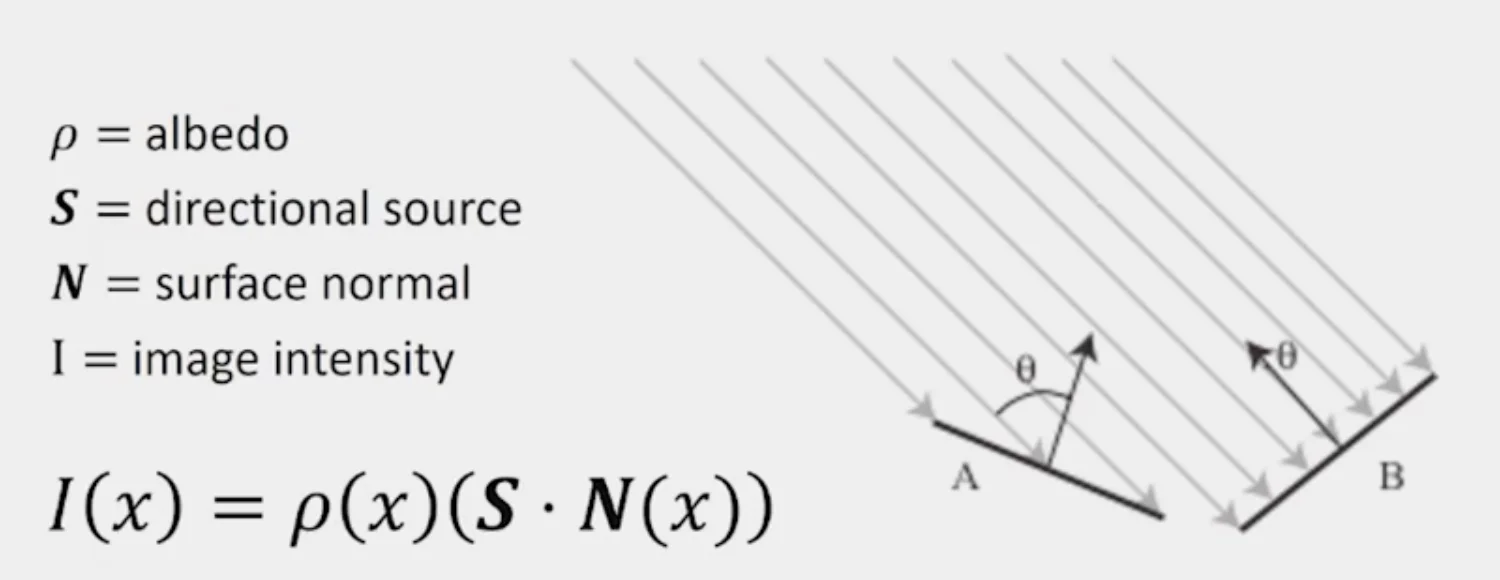
- Intensity depends on illumination angle
- less light comes in at oblique angles
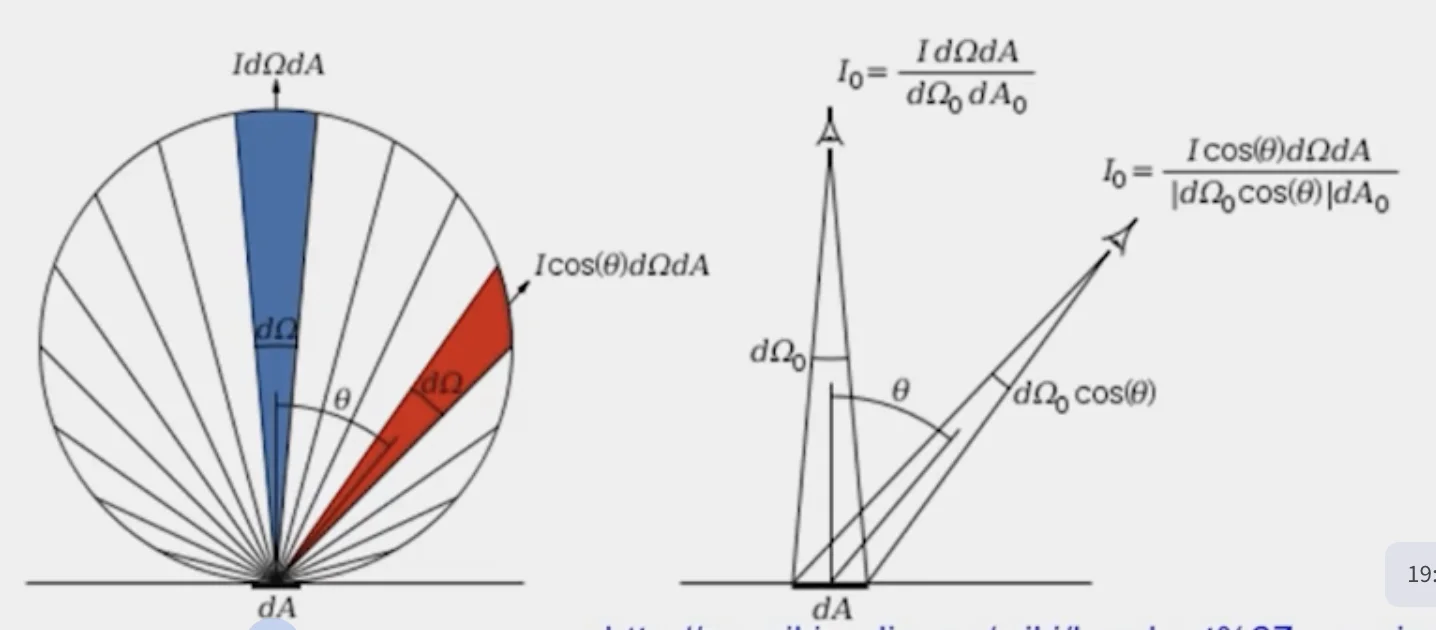
- However, perceived intensity does not depend on viewer angle
- The amount of reflected light are proportional to
- Visible solid angle also proportional to
Specular Reflection
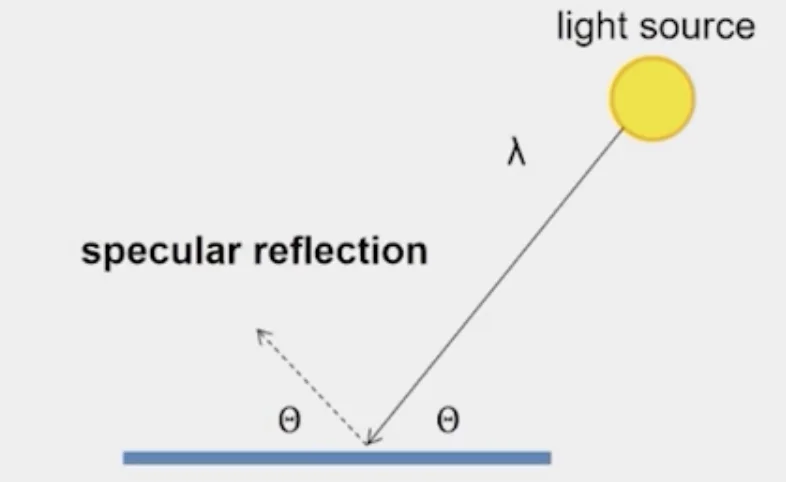
- Light reflected in one direction
- Reflected direction depends on light orientation and surface normal
- Specularity
- spot where specular reflection dominates (typically reflects light source)
BRDF
- Bidirectional reflectance distribution function
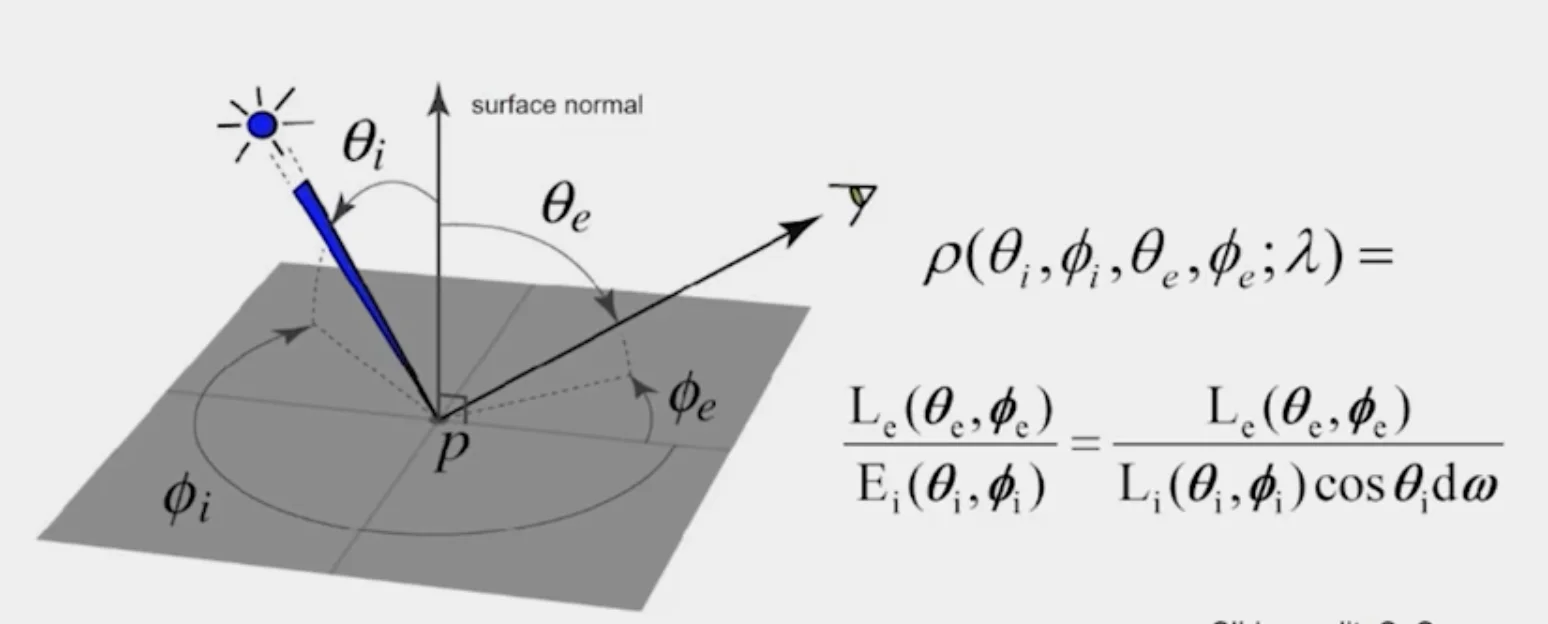
More complicated effects
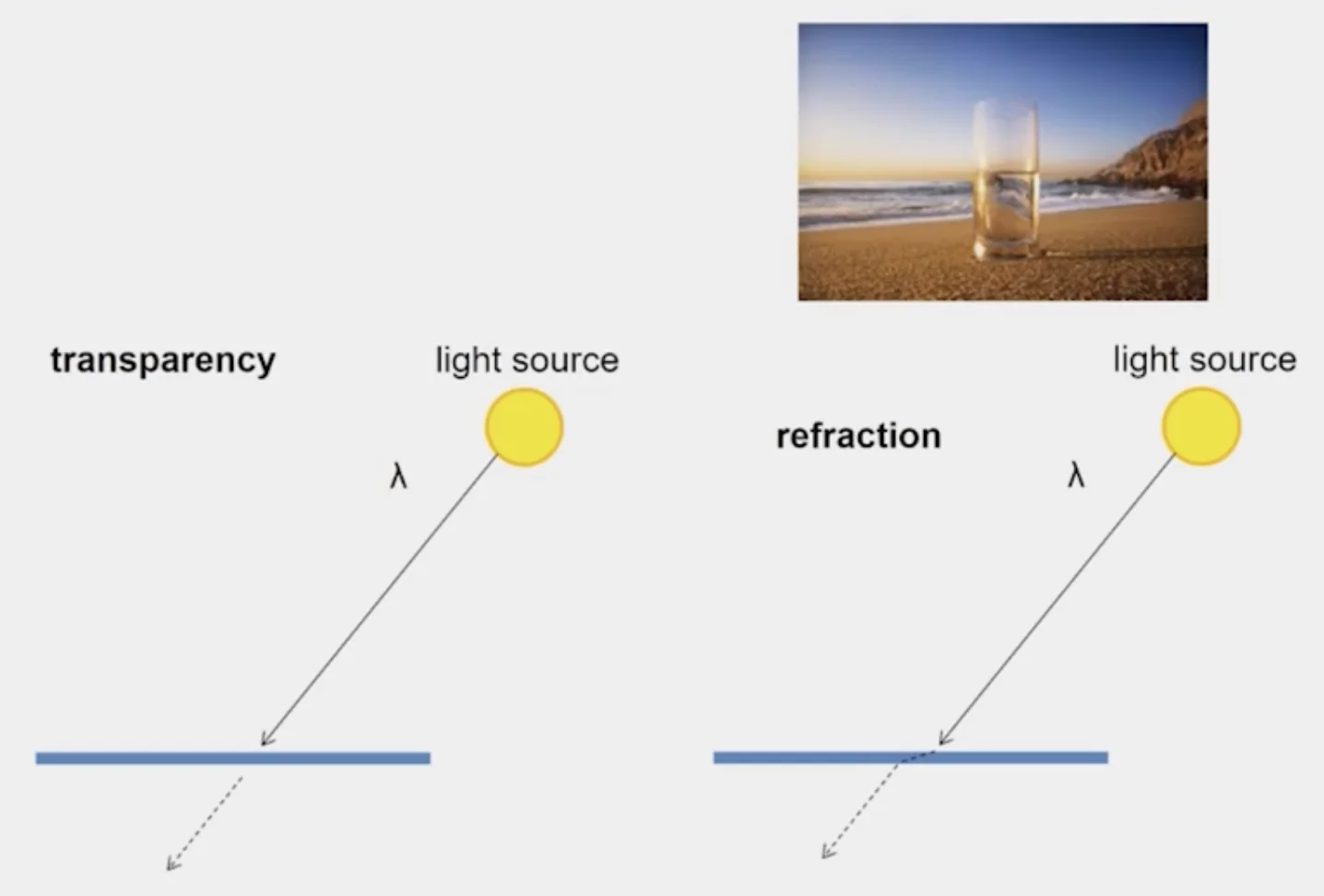
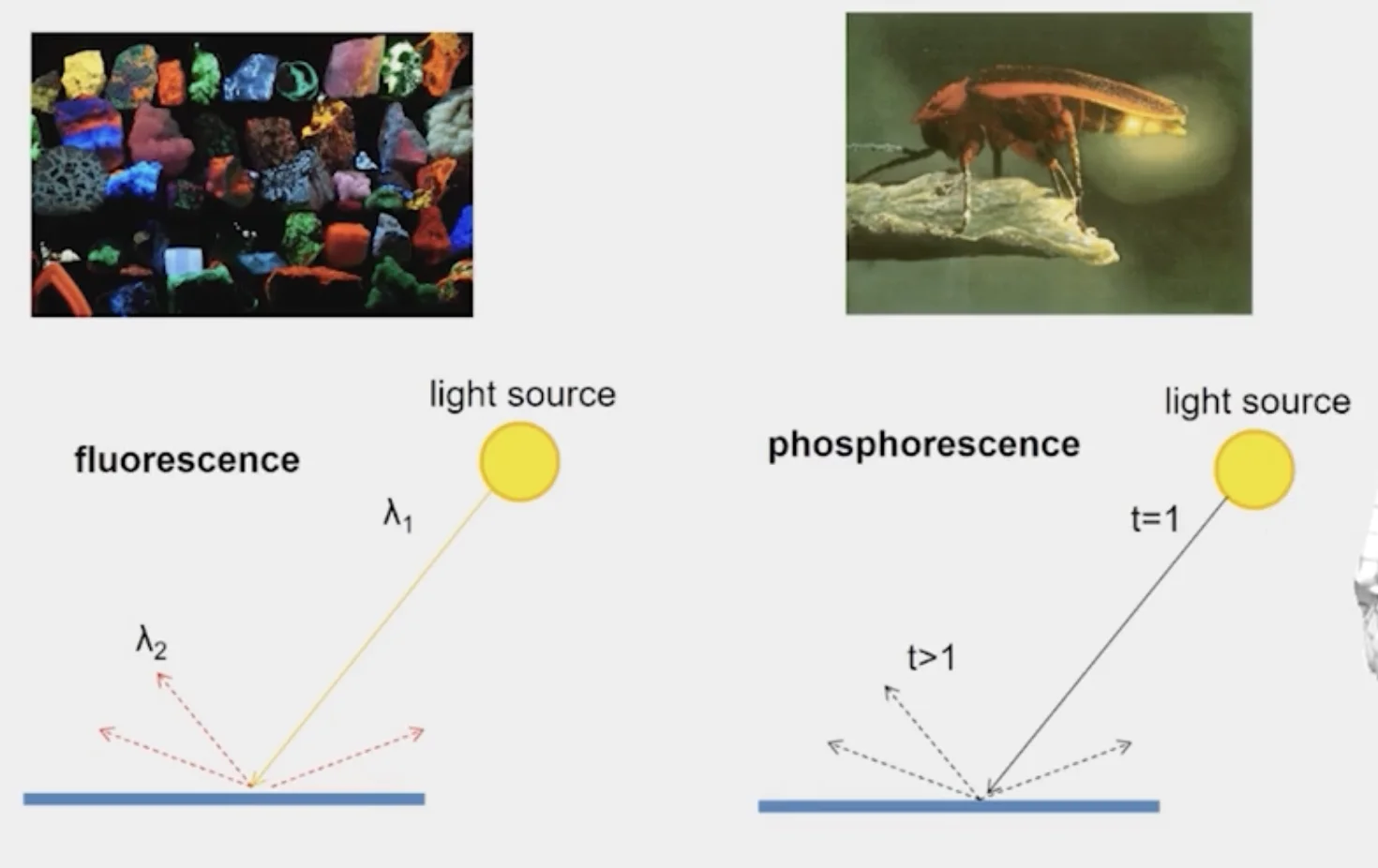
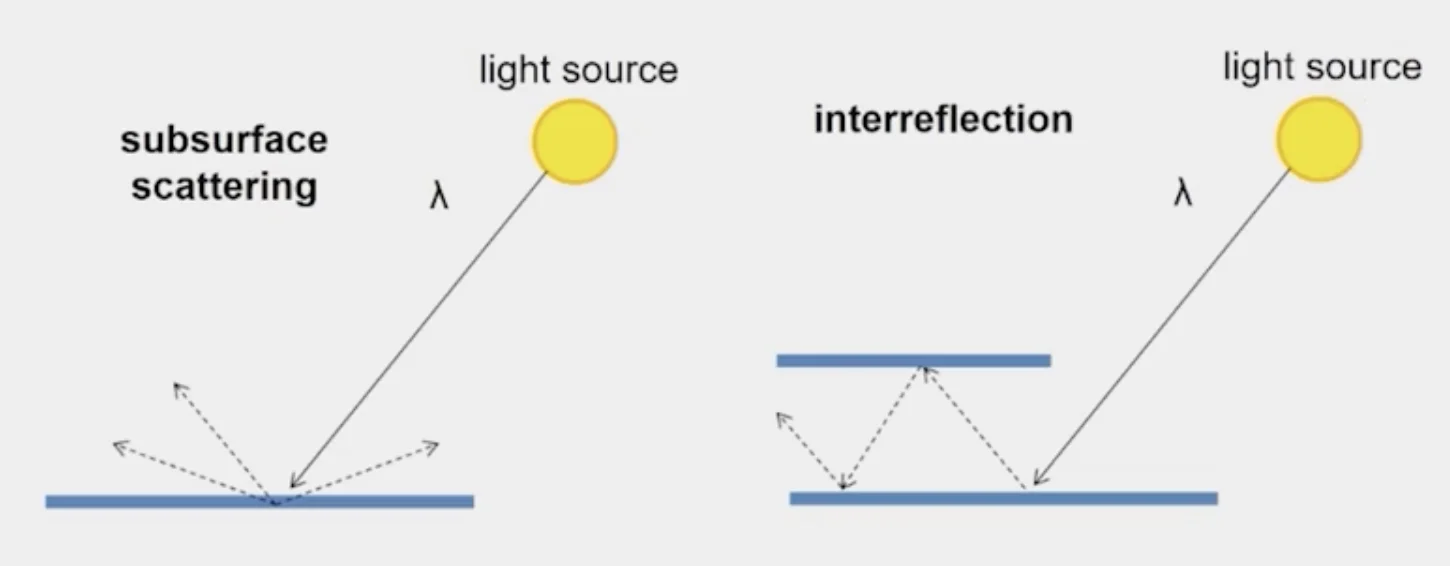
Things to remember
- Light has a spectrum of wavelengths
- Observed light depends on illumination intensities, surface orientation, material
- Every object is an indirect light source for every other
- Shading and shadows are informative about shape and position