5.1 Image Compositing
Feathering
Problems of simple cut and paste
- small segmentation errors noticeable
- pixels are too blocky
- won’t work for semi-transparent materials
Solution
- Near object boundary pixel values come partly from foreground, and partly from background
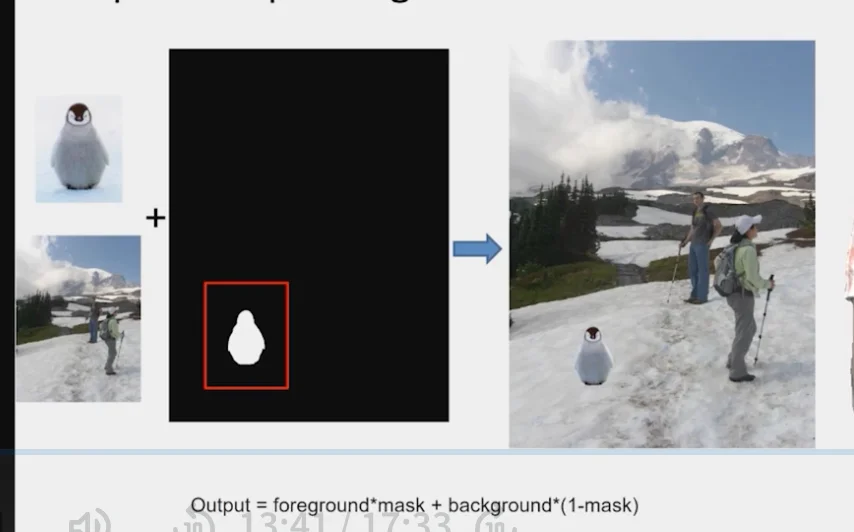
Output=foreground×mask+background(1−mask)
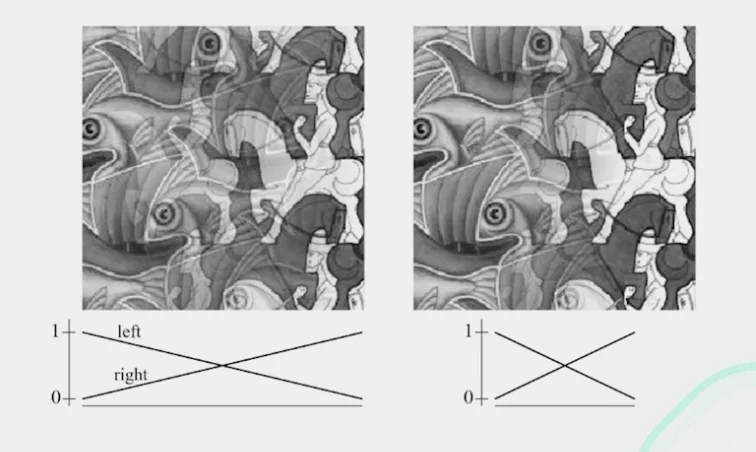
Alpha Blending/Feathering
Iblend=αIleft+(1−α)Iright
Too much feathering
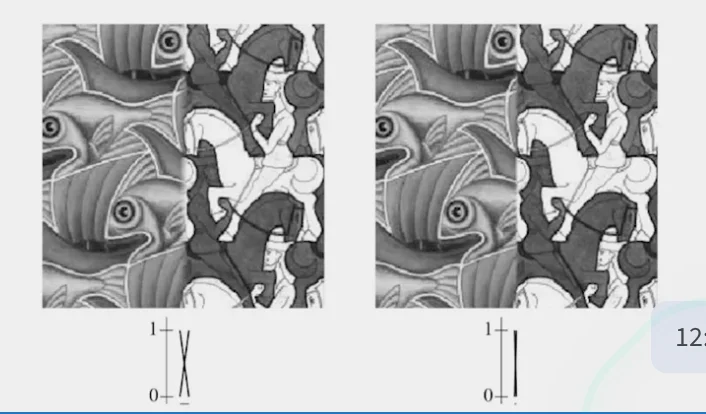
Too little feathering
Pyramid Blending
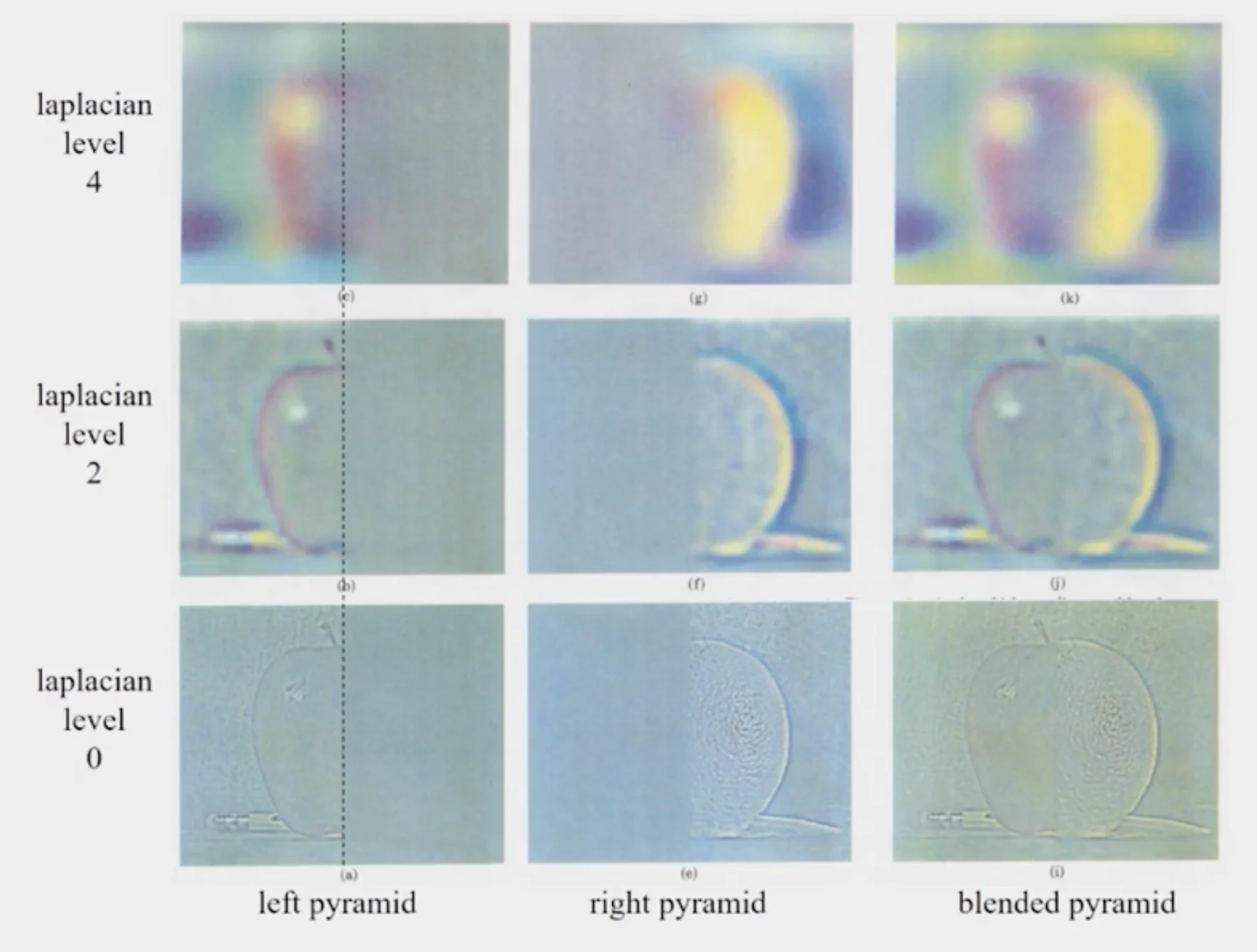
Laplacian Pyramid Blending
- Build Laplacian pyramids for each image
- Build a Gaussian pyramid of region mask
- Blend each level of pyramid using region mask from the same level
Ll2i=L1i⋅Ri+L2i⋅(1−Ri)
- Collapse the pyramid to get the final blended image
Poisson Blending
- A good blend should preserve gradients of source region without changing the background
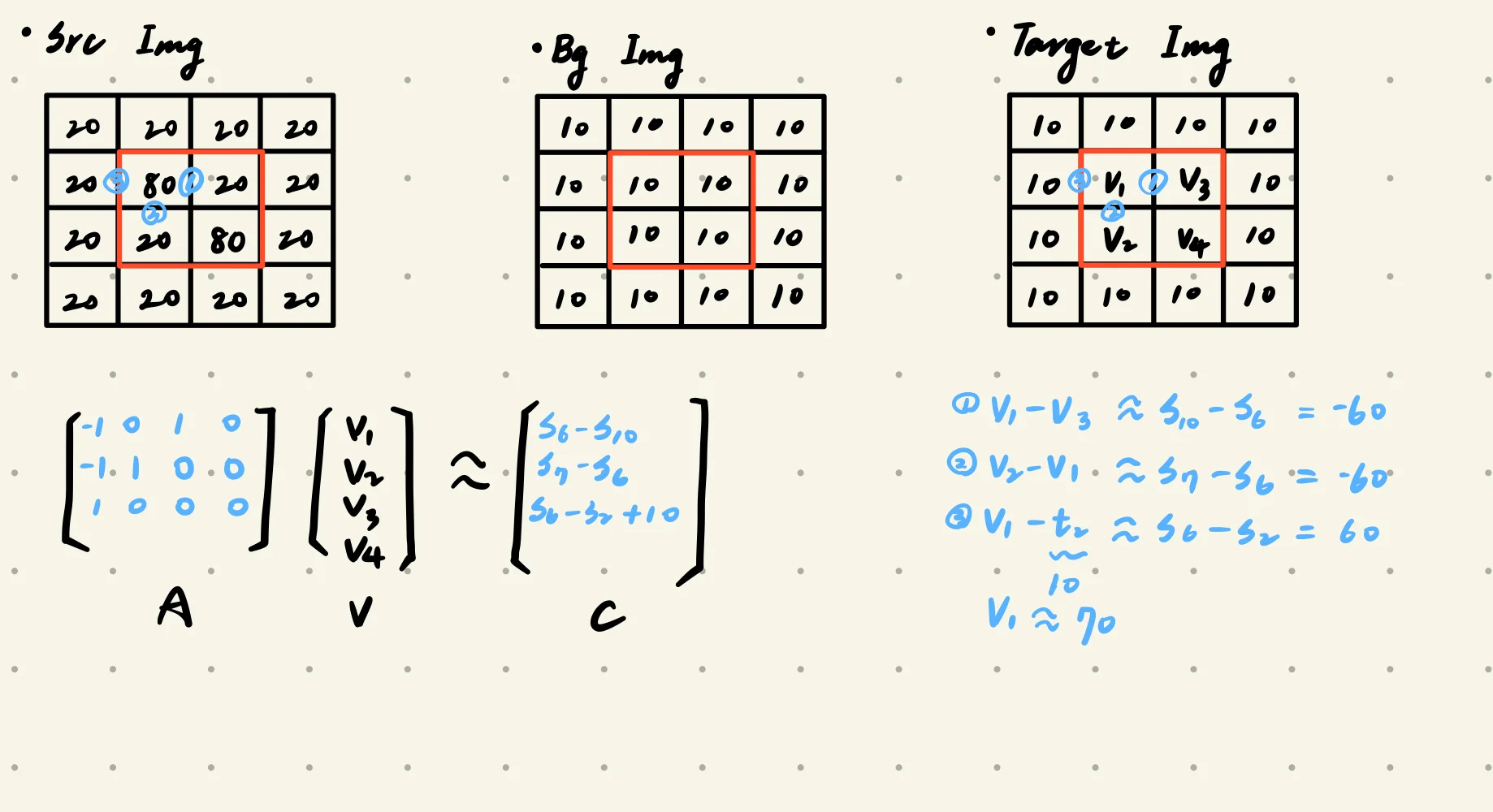
- Treat pixxels as variables to be solved
- Minimize squared difference between gradients of foreground and target regions
- Keep background pixels constant
v=vargmini∈S,j∈Ni,∩S∑((vi−vj)−(si−sj))2+i∈,j∈,∩¬S∑((vi−tj)−(si−sj))2
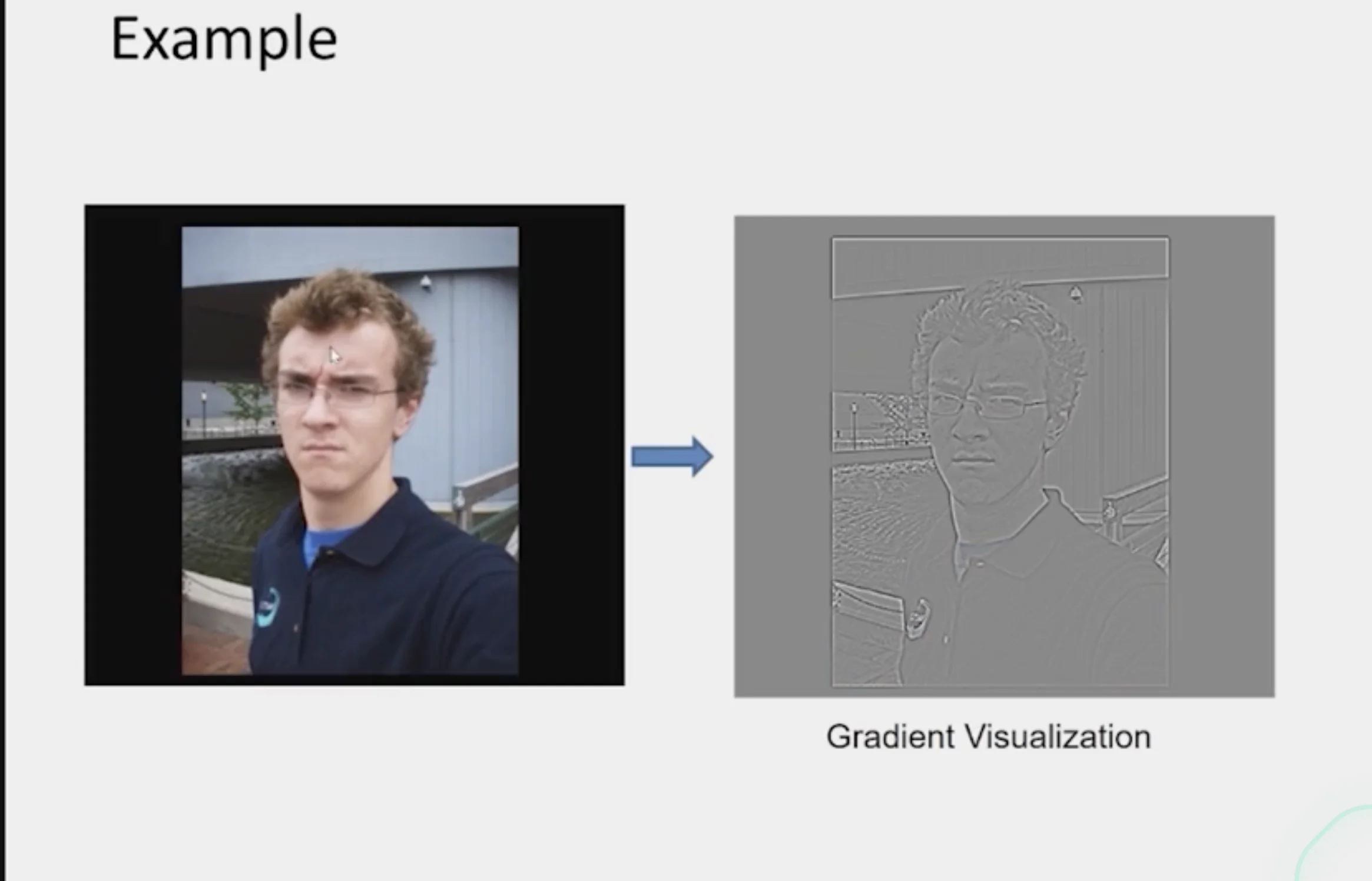
Gradient-domain Editing
- Instead of filtering the image, create a new image
- measures the directional change in pixel intensity
- Creation of Image
- A least squares problem in terms of
- Pixel intensities
- Differences of pixel intensities
Line Equation and Parameters
yi=mxi+b
Least Sqaures Objective
- This is the least-squares fitting problem
m∗,b∗=m,bargmini∑(yi−(mxi+b))2
Matrix Formulation
A=x11x21⋮xn1,v=[mb],c=y1y2⋮yn
{Av=cAv≈c(data is noisy)
v=vargmin∣∣Av−c∣∣2
∣∣Av−c∣∣2=(Av−c)⊺(Av−c)=v⊺A⊺Av−2c⊺Av+c⊺c
∇vE(v)=2A⊺(Av−c)=0⟹A⊺Av=A⊺c⟹v=(ATA)−1A⊺c
Example
v=vargmini∈S,j∈Ni,∩S∑((vi−vj)−(si−sj))2+i∈,j∈,∩¬S∑((vi−tj)−(si−sj))2
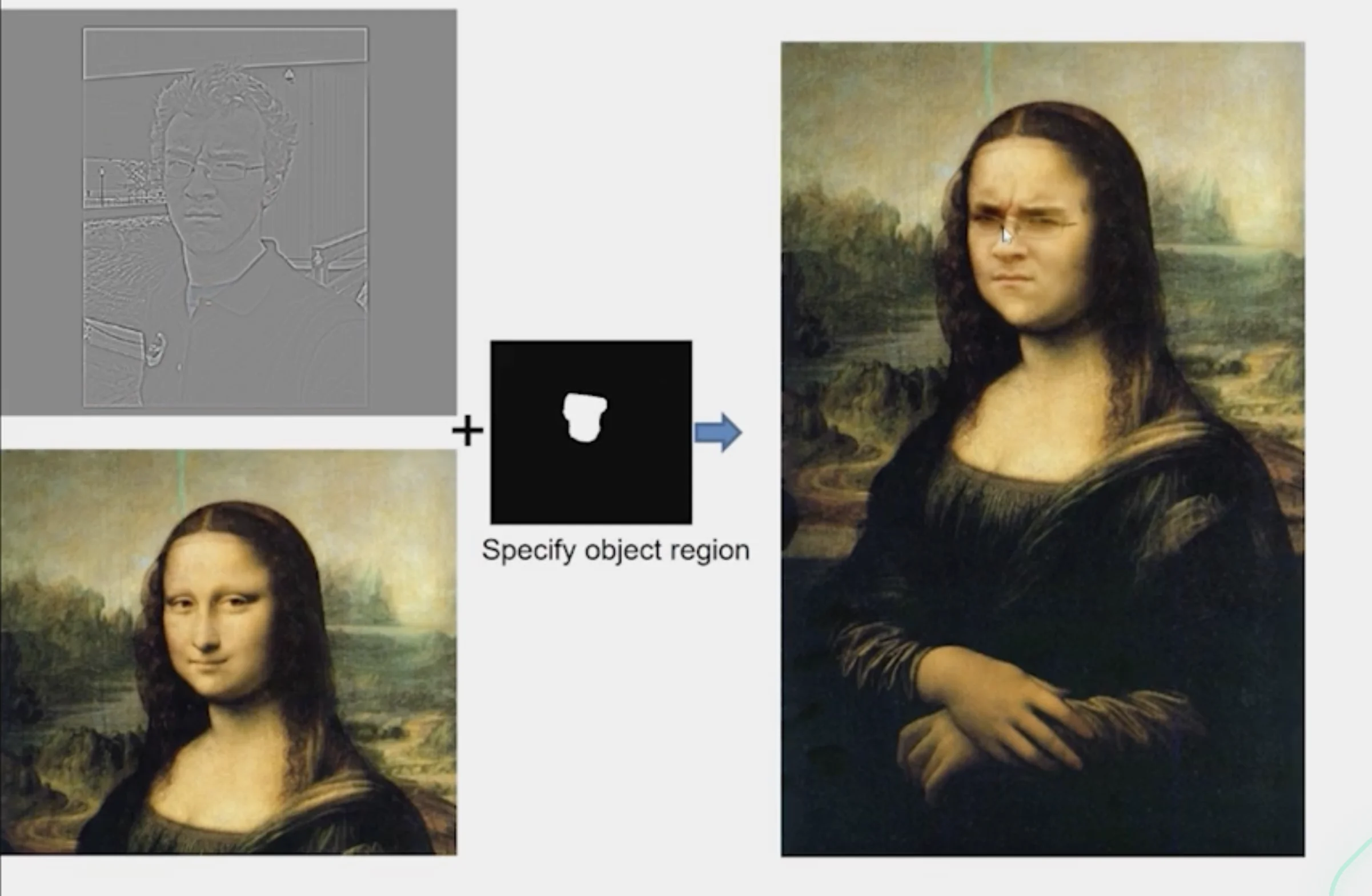
- source image:
- the image containing the object to be pasted
- background image:
- the image to be pasted to
- red:
- regions to be used to insert patch from the source image
Constraints
i∈S,j∈Ni,∩S∑((vi−vj)−(si−sj))2
- Inside the red region, the differences between neighboring pixels in the target should stay the same as in the source.
i∈,j∈,∩¬S∑((vi−tj)−(si−sj))2
- The difference between the pixels inside and outside the red regions should be the same in both the target image and the source image
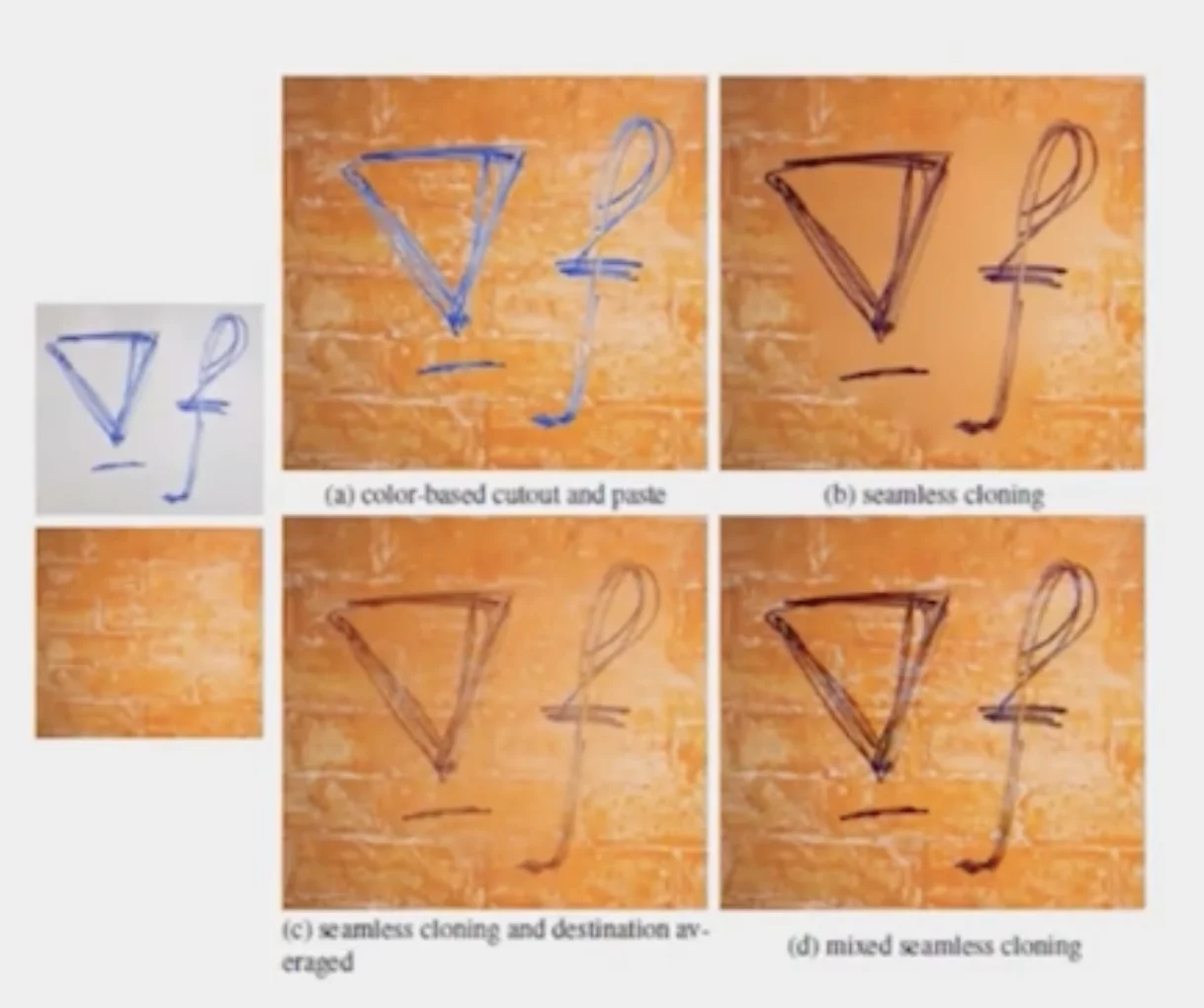
Some Results

Caution
What do we lose with Poisson Editing?
- We lose the texture of the source image in the target image
- Invariant to the overall color (only cares about the difference of color)
Blending with Mixed Gradients
- Use foreground or background gradient with larger magnitude as the guiding gradient
v=vargmini∈S,j∈Ni∩S∑((vi−vj)−dij)2+i∈S,j∈Ni,∩¬S∑((vi−tj)−dij)2
where
- dij is the gradient from source or target with larger magnitude
Things to Remember
1. Alpoha compositing
- Need nice cut (intelligent scissor)
- should feather
2. Laplacian pyramid blending
- Smooth blending at low frequencies, sharp at high frequencies
- usually used for stitching
3. Gradient domain editing
- Also called Poisson Editing
- Explicit control over what to preserve
- Changes foreground color
- Applicable for many things besides blending








