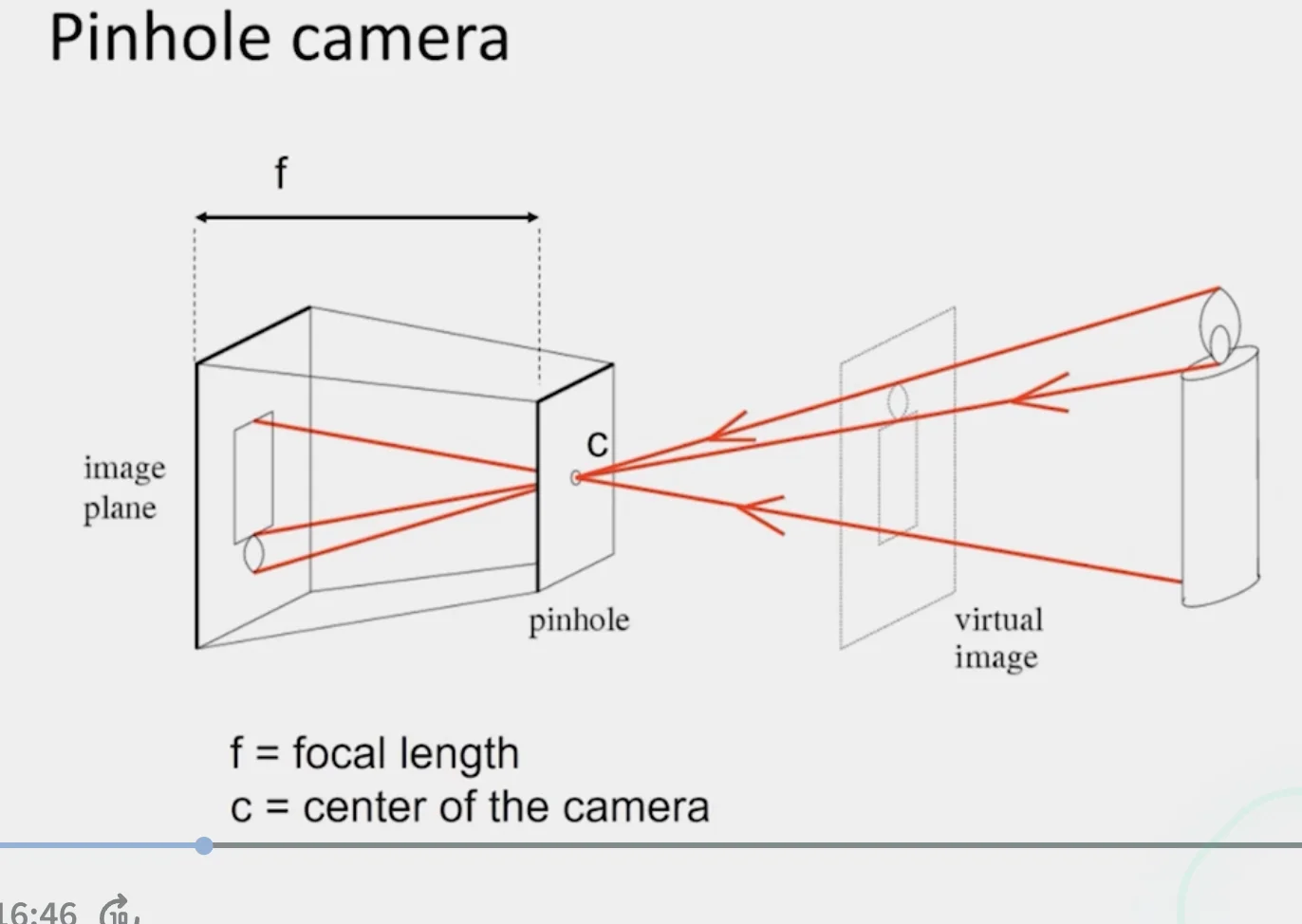
6.2 Pinhole Camera
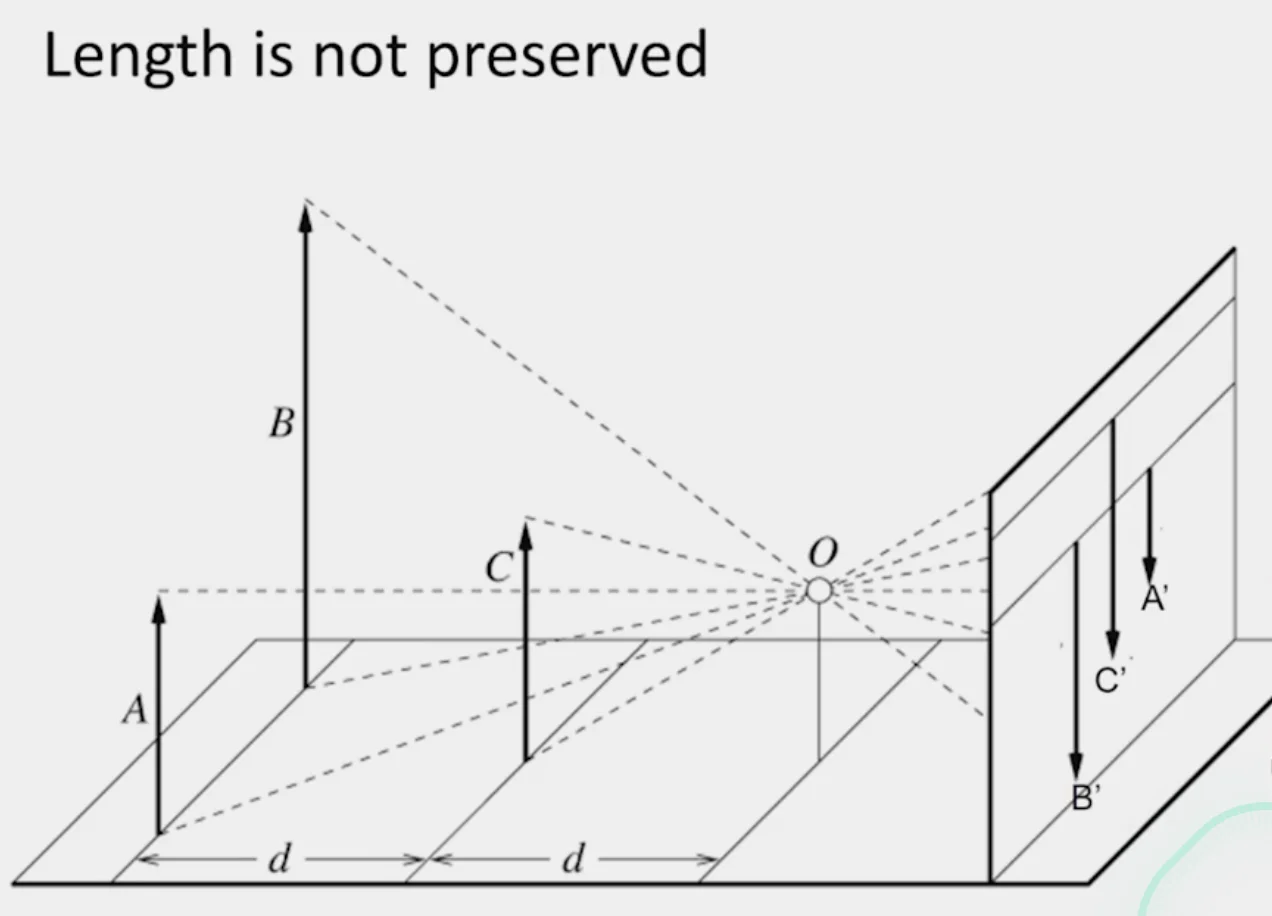
Projective Geometry
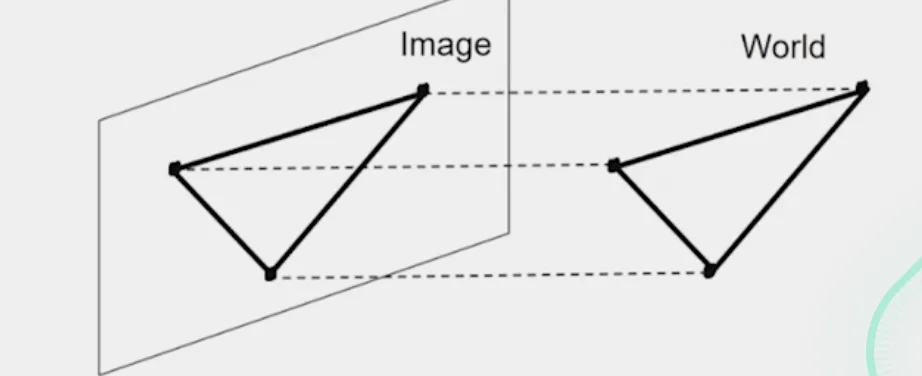
- Angless and length are lost
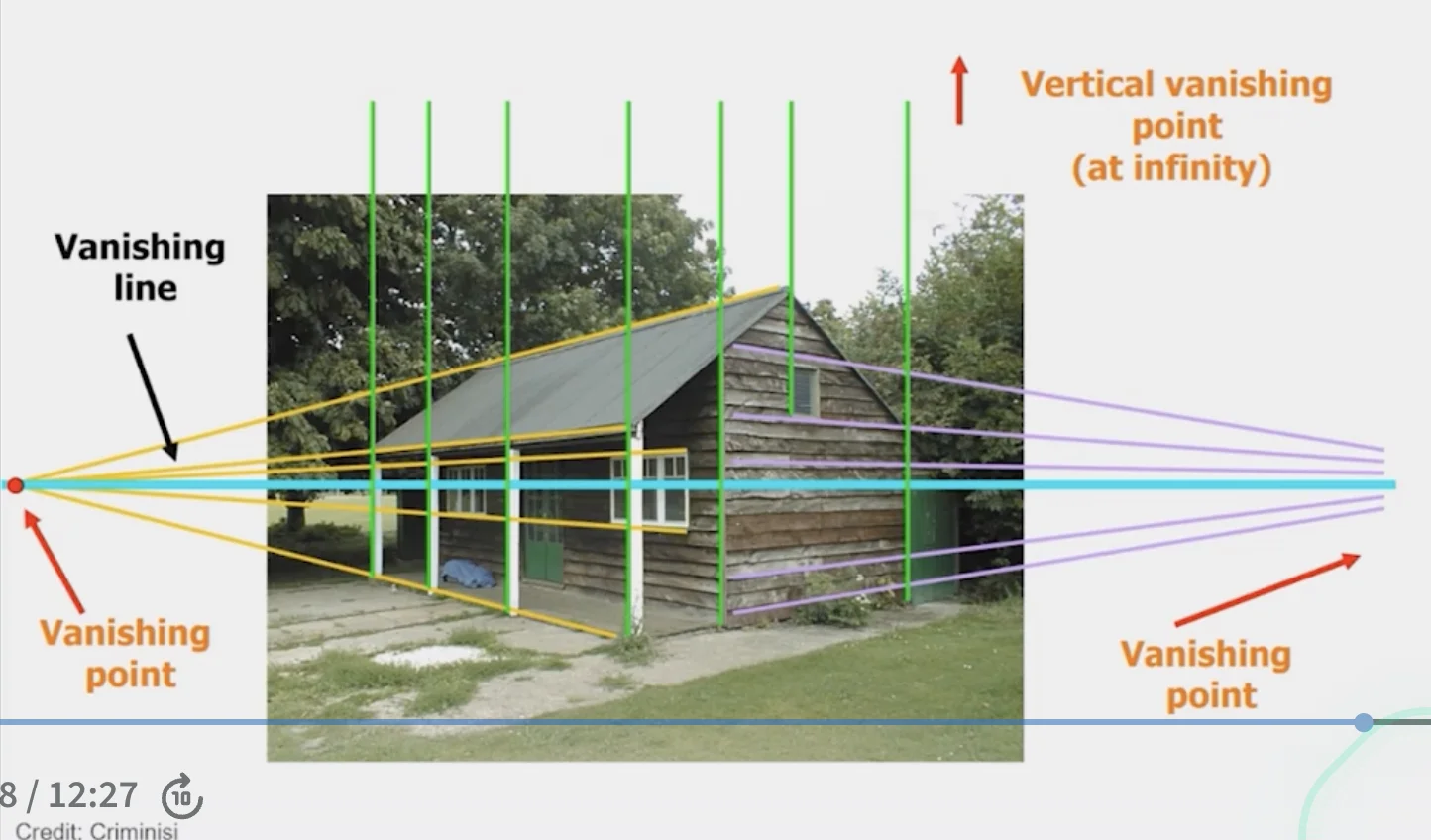
Vanishing Points and Lines
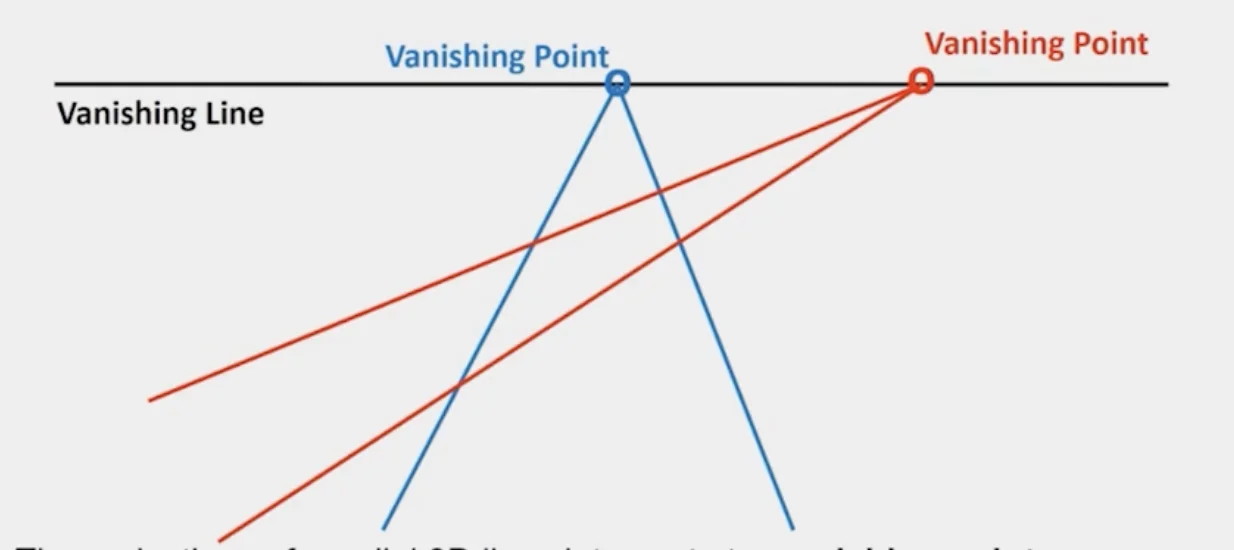
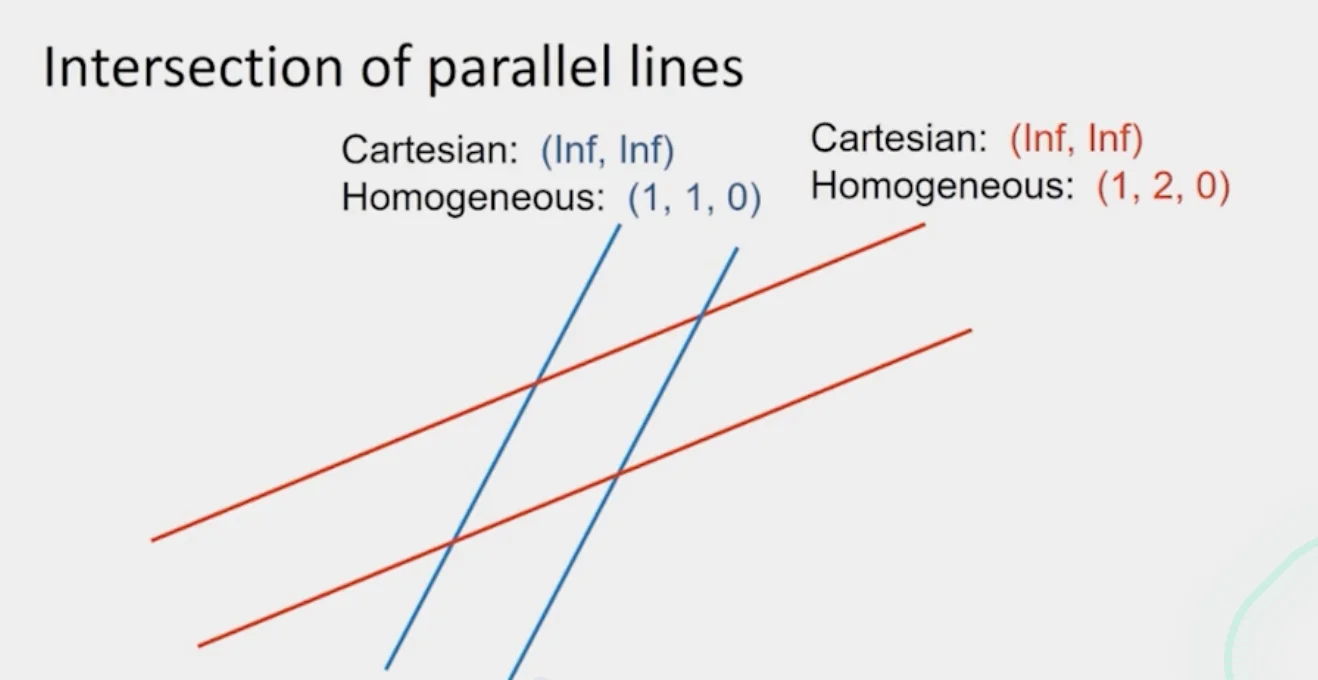
- The projections of parallel 3D lines intersect at a vanishing point
- vanishing point → 3D direction of a line
- The projections of parallel 3D lines intersect at a vanishing line
- vanishing line → 3D orientation of a surface
- If a set of parallel 3D lines are also parallel to a particular plane, their vanishing point will lie on the vanishing line of the plane
Projection: world coordinates → image coordinates
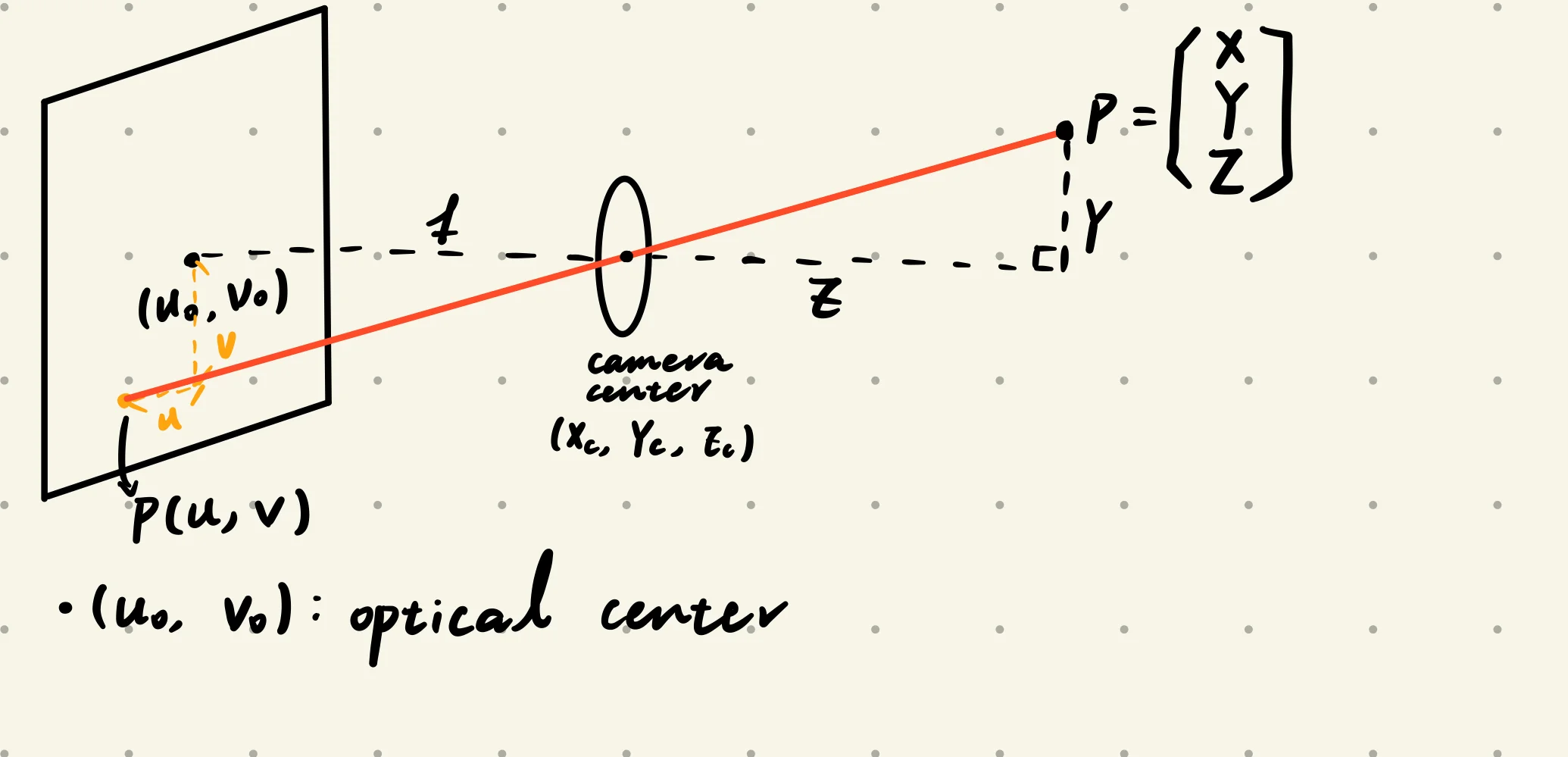
ZY−Yc=fv−v0v=fZY−Yc+v0u=fZX−Xc+u0
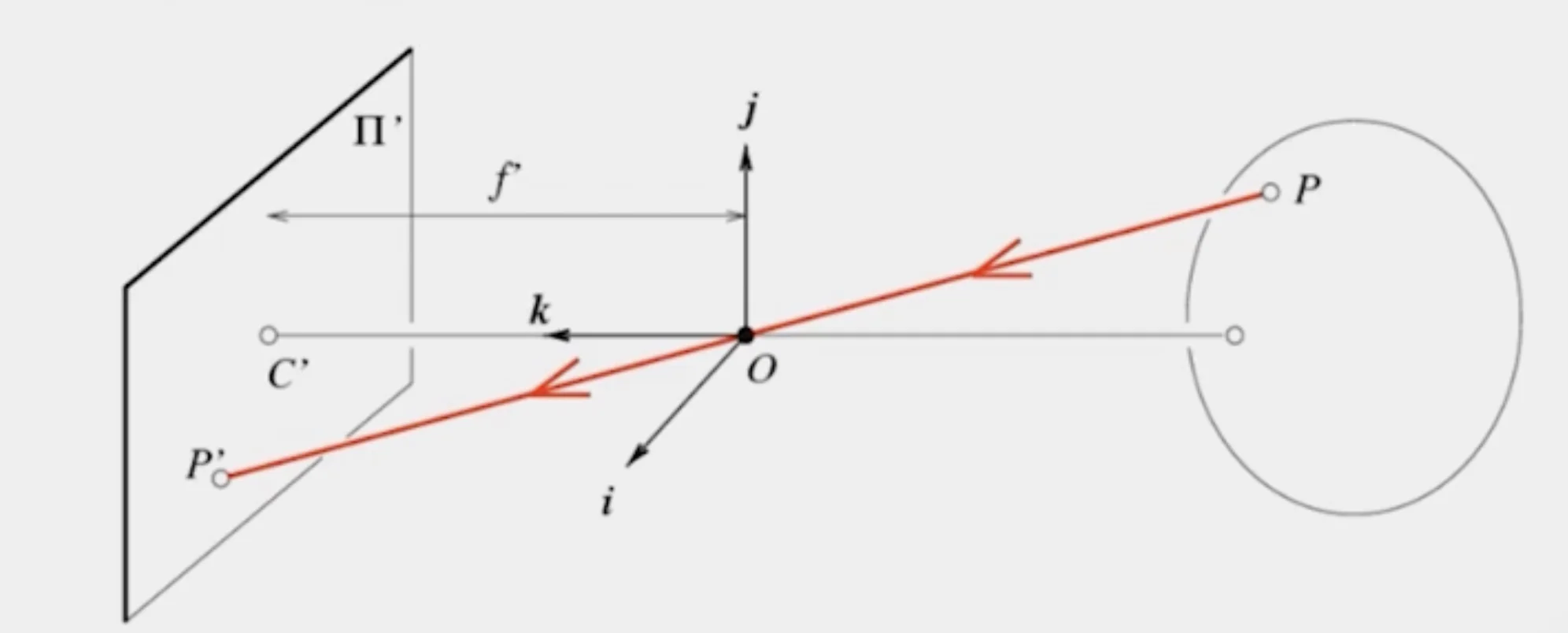
Projection Matrix
{wu=fxwv=fy(w=z)⟹{u=zfxv=zfy
- Intrinsic Assumptions
- Unit aspect ratio
- Principal point at (0, 0)
- No skew
- Extrinsic Assumptions
- No rotation
- Camera at (0, 0, 0)
x=K[I0]X⟹wuv1=f000f0001000xyz1
where
K=f000f0001
If not at (0, 0)
K=f000f0u0v01(u=zfx+u0)
If pixels are not square
K=α000β0u0v01({α:scale of focal in x directionβ:scale of focal in y direction)
If pixels are skewed
K=α00sβ0u0v01
Allow Camera Translation
x=K[I∣t]X⟹wuv1=α000β0u0v01100tx010ty001tzxyz1
Warning
xyz1
is not the camera center. It is the amount of 3D points that have to have to move in order to enter the camera’s coordinates
Allow camera rotation
x=K[R∣t]X⟹wuv1=α00sβ0u0v01r11r12r13txr21r22r23tyr31r32r33tzxyz1
Important
- Matrix R is orthonormal
- DoF
- Intrinsic matrix: 5
- Extrinsic matrix: 6
Vanishing Point = Projection from infinity
p=K[Rt]xyz0=KRxyz=KxRyRzR
wuv1=f0u00fv0001xRyRzR⟹{u=zRfxR+u0v=zRfyR+v0
Orthographic Projection
- Special case of perspective projection
- used when the scene is far away or depth variation is small.
- It assumes parallel projection rays
- All lines of sight are parallel, not converging.
uv1=100010000u0v01xyz1
Scaled Orthographic Projection
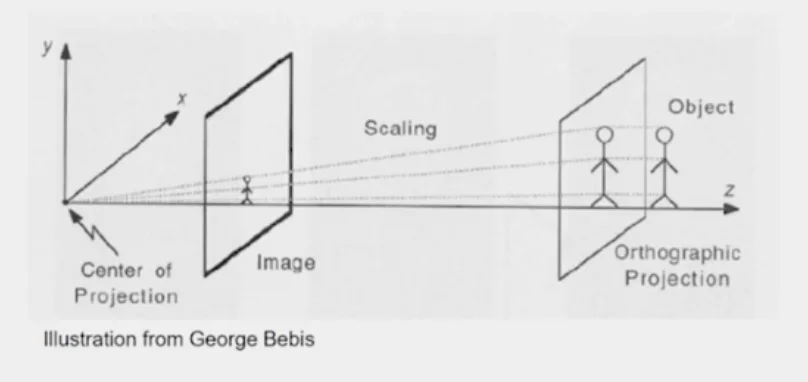
- weak perspective
- Assume that all points in the object are roughly at the same average depth Z0
- Perspective effects are approximated by a constant scale factor.
x=sX,y=sY
where
- s=Z0f
uv1=10001000000sxyz1
Summary
| Model | Projection Equations | Notes |
|---|
| Perspective | x=ZfXy=ZfY | Realistic camera model; nonlinear; introduces foreshortening and vanishing points. |
| Scaled Orthographic (Weak Perspective) | x=sXy=sYs=Z0f | Linear approximation of perspective; assumes small depth variation; preserves shape ratios. |
| Orthographic | x=Xy=Y | Simplest linear model; no scaling or depth effect; preserves parallelism and true dimensions. |
Tip
Homogeneous coordinates allows 3D world points mapped to 2D image points in a linear way








