numpy
Important
This note compiles numpy-related codes with detailed expalanation
Moving Average
def moving_average(
self,
positions: list[tuple[float, float]],
window_size: int = 5,
pad_mode="edge",
) -> list[tuple[float, float]]:
# list to numpy array
pos = np.asarray(positions, dtype=float)
# create kernels(weights) for averaging
k = np.ones(window_size) / window_size
# half the window size, so we can pad equally on both sides.
pad = window_size // 2
x = np.pad(pos[:, 0], (pad, pad), mode=pad_mode)
y = np.pad(pos[:, 1], (pad, pad), mode=pad_mode)
xs = np.convolve(x, k, made="valid")
ys = np.convolve(y, k, mode="valid")
return list(zip(xs, ys))Padding
x = np.pad(pos[:, 0], (pad, pad), mode=pad_mode)
y = np.pad(pos[:, 1], (pad, pad), mode=pad_mode)pos[:, 0]: all x-coordinatespos[:, 1]: all y-coordinatesnp.pad(..., (pad, pad), mode="edge")
# example: pad = 2, mode = "edge"
# two 10s before x and two 30s after x
Original x: [10, 20, 30]
Padded x: [10, 10, 10, 20, 30, 30, 30] (edge values repeated)Convolution
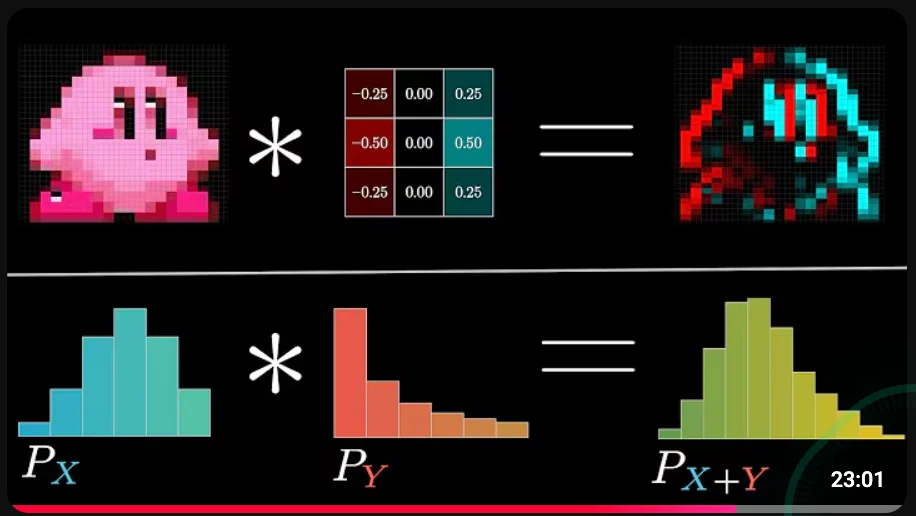
xs = np.convolve(x, k, made="valid")
ys = np.convolve(y, k, mode="valid")Modes
-
"valid": only return results where the kernel completely overlaps with the input array (no partial windows at the edges) -
"full": returns all positions, including where the kernel only partly overlaps the data -
"same": returns output the same length asx(centered on input) -
Examples:
import numpy as np
data = [1, 2, 3]
kernel = [1, 1, 1] # window size 3
# [1 3 6 5 3] (longest output)
np.convolve(data, kernel, mode="full")
# [3 6 5] (same length as data)
np.convolve(data, kernel, mode="same")
# [6] (only one place where kernel fully fits without padding)
np.convolve(data, kernel, mode="valid")Displacement
displacements = np.linalg.norm(
np.diff(positions, axis=0),
axis=1,
)np.diff(position, axis=0)- for each column in this 2-D array, calculate the difference between every two elements
np.linalg.norm(diff, axis=1)- for each row in this 2-D array, compute the vector length across its columns.
array vs asarray
- The definition of
asarray
def asarray(a, dtype=None, order=None):
return array(a, dtype, copy=False, order=order)asarrayreturns an array with fewer options, and does not copy the original array be defaultarraycopys the original python list by default.
Sparse Matrix
# Create a sparse matrix
m, n = 4, 5
A = lil_matrix((m, n), dtype=float)
# Assign a few entries (sparse pattern)
A[0, 1] = 10.0
A[0, 4] = 2.5
A[1, 1] = -3.0
A[2, 0] = 7.0
A[2, 3] = 1.2
A[3, 2] = 5.5After assignments
- LIL structure (row -> list of (col, val))
row 0: [(1, 10.0), (4, 2.5)]
row 1: [(1, -3.0)]
row 2: [(0, 7.0), (3, 1.2)]
row 3: [(2, 5.5)]- Dense view
[[ 0. 10. 0. 0. 2.5]
[ 0. -3. 0. 0. 0. ]
[ 7. 0. 0. 1.2 0. ]
[ 0. 0. 5.5 0. 0. ]]Convert to CSR (Compressed Sparse Row)
A_csr = A.tocsr()
A_csr.data
A_csr.indices
A_csr.indptr- CSR internal arrays
data: [10. 2.5 -3. 7. 1.2 5.5]
indices: [1 4 1 0 3 2]
indptr: [0 2 3 5 6]