What’s that?
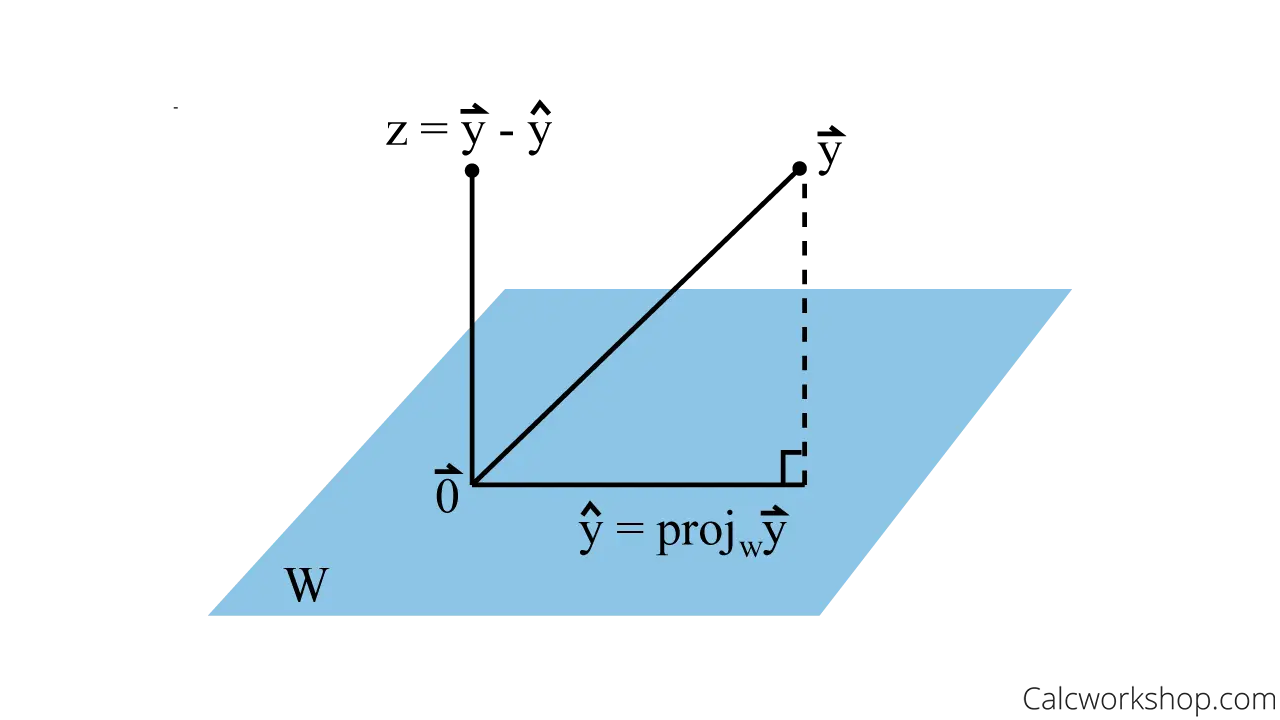
Let V be a subspace of Rd. Then any vector w∈Rd can be uniquely decomposed as:
w=w∣∣+w⊥
where
- w∣∣∈V
- w⊥∈V⊥
- V⊥={v∈Rd:v⊺u=0∀u,u∈V}
Proof
- Let V=span{x(i),…,x(N)}
1. Define w∣∣ as an orthogonal projection
w∣∣=projV(w)
- projV(w) is a unique vector that is closest to w (minv∈V∣∣w−v∣∣)
2. Define w⊥
w⊥=w−w∣∣
3. Show w⊥⊥V
By the properties of orthogonal projection, w⊥ is orthogonal to every vector in V.
w⊥⊺x(j)=(w−w∣∣)⊺x(j)=0
Express w∣∣ in terms of basis vector
Since w∣∣∈V=span{x(1),…,x(N)}, by definition of span:
w∣∣=j=1∑Nα(j)x(j)
for some coefficient α(1),…α(N)∈R
